What are Botnets?
First of all, we thought it would be convenient to express what botnets are in the simplest way possible. It is no more and no less than a series or collection of compromised computers connected to the internet, each of which is running one or more bots. Then, when an attacker succeeds in endangering a computer, there is usually a code (inside the malware) that “commands” it to become part of a botnet. So, the so-called “Botmaster” or “Botderder” controls these computers, so that it jeopardizing them by means of standard-based network protocols, such as IRC and HTTP.
More in depth, let’s talk about the three types of hacker attacks:
- Low-risk: These are unsophisticated attacks that do not generate financial damage and do not steal data.
- Medium/higher risk: These are the type that happen when our computer is connected to a botnet, making it part of a criminal network.
- Critical risk: it’s about the installation of software, stealing data from us and, in the worst case, money from our financial accounts. Let us clarify that this higher risk, occurs when our computer has been added to a botnet.
On the other hand, but in the same conceptual direction, let’s note that botnets can be used to carry out a distributed service generation attack, which is also called DDoS and so on:
- Obtain the data they are looking for.
- Send spam.
- Grant access to the attacker, to the target-device and its connection.
The botnet owner can now control it using the command and control software, which is also called “C & C”. Let’s note, by the way, that the word “Botnet” is a fusion or combination of “Robot” and “Network”, that is normally used with a negative and malicious connotation. Once the previous fundamental concepts have been developed, we will go into some depth to state that a botnet is a logical collection of devices connected to the Internet, such as smartphones or loT devices, whose security has been attacked and violated, and the control has been transferred to a third party.
Each of these compromised devices is known as “Bot”, and it is created when it gets penetrated by malware, i.e. malicious software. The owner and/or controller of a botnet is able to direct, almost at will, the activities of such compromised devices through communication channels that are structured using standards-based network protocols, such as IRC and also the so-called “Hypertext Transfer Protocol” or HTTP. It should also be taken into account that botnets are increasingly rented by cyber-criminals, in their unfortunate quality of highly demanded products, for a variety of purposes or purposes.
As far as the Botnet Architecture is concerned, let’s say it has evolved as an effort to elude detection and disruption. Traditionally, bot programs have been built as clients, which communicate through pre-existing servers, allowing the bot administrator himself to carry out all the control from a remote location. However, as far as the most recent botnets are concerned, we must bear in mind that they currently rely on the so-called pre-existing “Peer-to-Peer Networks” to communicate. These P2P programs (bots) carry out the same actions as the client-server model and do not require a central server for communication purposes.
In this image we can see the client-server model:
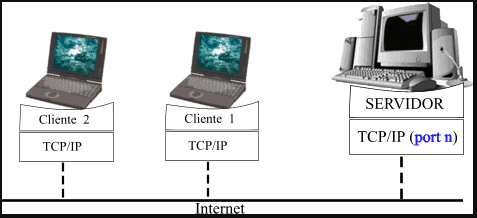
Source: Definición ABC
Based on the previous image, we see that a network is based on the server-client model, in which individual clients request resources and services from centralized servers, while the first Internet botnets used the same client-server model to carry out their respective tasks. Usually, these botnets operate through networks, domains or, through Relay Chat websites. This way malware-infected clients access a default location and wait for incoming commands from (towards) that server. The bot administrator then sends certain commands to the server and, in turn, transmits them to the clients, who execute the commands and, in turn, report their results to that administrator.
Let’s see, this time, what has to do with IRC botnets, to see that the infected clients are connected, precisely, to an infected IRC server, at the same time that they join a channel that has been designated, a priori, for C & C by the bot “pastor”. The Bot Herder then sends the commands to the channel via the IRC server, while each client retrieves those sent commands and executes them. To complete the process, customers send certain messages to the IRC channel, including the results of their respective actions executed. Let’s look, this time, at an image of Peer-to-Peer (P2P):
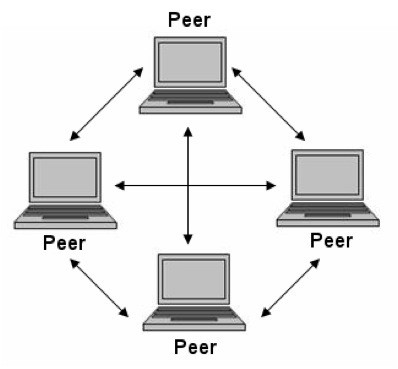
Source: NEO-University of Málaga
As we can see, a Peer-to-Peer (P2P) network in which, by the way, interconnected nodes or “Peers” share resources with each other, is established without the need for a centralized administrative system. Now, to find other infected devices, the bot does a discreet probing of IP addresses, until it gets in touch with another infected machine. Thus the bot that has been contacted responds with information, such as its software version and a list of known bots. If one of the bots is lower than the other, a file transfer is started to update so that each bot increases its list of infected machines, and at the same time it is updated by communicating periodically with all known bots.
Regarding the most important components of botnets, we have:
- The “Zombie” computer: in the field of informatics, a zombie computer is a computer connected to the Internet and that has been intervened or compromised by a hacker, by means of a computer virus or a trojan. It can also be used to perform malicious tasks remotely. Zombie botnets are usually used (mostly) to spread spam and also to launch denial-of-service attacks. The vast majority of the owners of “zombie” computers are unaware that their system is being infected or used in such a way. This whole process is often called “Scrumping”.
- Control protocols: IRC is a traditional means of C & C, thanks to its communication protocol. To be more explicit, let’s note that a bot manager creates an IRC channel, so that infected clients can join. Messages sent to this channel are then transmitted to all members of this channel. And the administrator has the possibility to configure the channel theme to command the botnet.
Monitoring tools for a network of computers: when we believe that they do not work because of Botnets
Regarding this subtitle, there is an inescapable question: is there any way to detect that a computer is being used in a DDoS botnet-based attack? Others may ask the following alternative question: Is there a tool such as software that is capable of detecting strange and/or unusual traffic exploiting the activity of that (apparently) attacked computer? The answer is that there is currently no easy way to detect it. However, there are defences in the field of prevention:
- First, we should avoid infection. Much has been said and written about ways to prevent security breaches. For example, countless security guides have been written for inexperienced users, such as “Secure Linux Desktop”. However, it is best to think about what elements we would include and at what depth. There are issues that may seem obvious and can be overlooked, but they should be taken into account. For example, it is highly recommended that people read the “Consumer Report Online Safety Guide”, as it covers many items that we need to know.
- Secondly, user behaviour must be cautious, even to the extent that it is necessary:- Adopt good password practices: we should all choose two very strong passwords, and use them like this: one for the email account(s), seriously considering that we should never have the same password for two or more email accounts (if we have more than one). And, on the other hand, another password for other activities that we usually display on the Net, such as registering on websites and other similar ones. For the issue of passwords for bank accounts and international payment gateways (such as Paypal, Payonner, Skrill and so on), it will be highly recommended to choose passwords that are different from the previous ones and which, by the way, are very secure, having more than 9 or 10 characters, combining uppercase, lowercase, numbers and some symbols.
Let’s also highlight that everyone should be aware that anyone who knows an email password has access to bank accounts, Facebook and many other Internet services.- Use the password manager of the browser(s) we use, taking advantage of the fact that these administrators allow us not to memorize the passwords. Now, when the browser asks us if we allow you to remember the password, the answer must be “yes”. Once we grant this authorization, we may choose complex passwords that are difficult to guess by third parties.- We need to know where we enter our passwords: we need to mark sensitive websites on the security issue, such as banks and email account providers. When we log in to them, we must click on the bookmark and then enter the password.– We should never download software from unknown sites to avoid receiving malicious programs.
– When surfing the net, you need to look up and to the left: we must look at the address bar of the browser, to identify the domain name of the site we are navigating through, and avoid surprises. If we are going to enter personal information into that website and have questions about who will receive it, this bar will find the answer..
- Thirdly, we must administer the system: to that end, it is necessary:
– Work with a safe browser. Chrome is the most recommended, while if you want to work with Firefox, it is best to install HTTPS Everywhere.
– Enable automatic updates, to make sure that the best patched version of all software is always running.
– Enable automatic backups without your participation.
– If our operating system is Windows, you need to install a free antivirus or, in other words, don’t trust the preloaded software that is a trial version, whose license expires after a while. And once it’s expired, we’ll be unprotected. Avast and Avira are the most recommended free antivirus programs. If you have a Mac, you don’t need to install any antivirus software.
Finally, let’s note that in Pandora FMS we can also find valuable and detailed information, regarding this botnets topic and, about the ways we can monitor our networks in order to implement the necessary actions to avoid being infected. Being part (unknowingly) of a botnet is very dangerous for the security of our data and, above all, our financial resources.
About Pandora FMS
Pandora FMS is a flexible monitoring system, capable of monitoring devices, infrastructures, applications, services and business processes.
Of course, one of the things that Pandora FMS can control is the hard disks of your computers.
Would you like to know more about what Pandora FMS can offer you? Discover it by entering here: https://pandorafms.com
If you have more than 100 devices to monitor, you can contact us through the following form: https://pandorafms.com/en/contact/
Also, remember that if your monitoring needs are more limited you have at your disposal the OpenSource version of Pandora FMS. Find more information here: https://pandorafms.org
Rodrigo Giraldo, freelance technical writer. Lawyer and astrobiology student, he is passionate about computers, reading and scientific research.