Best Network Tools to manage your network
Today, we’re going to bring you a compilation of all those network tools you should know about in order to correctly manage your networks. Many of these network tools have been around for some time, but they all continue evolving and are still used in productive environments. They’re free, or at least have an open version. On another note, we’d be delighted to receive new proposals for us to evaluate and add to the list. Drop your commentaries letting us know which network tools you think are the best, and which of those you’d add to our list. We want to hear from you!
Network toolkit
In this section we’ll tell you about the most important open or free network tools that you should add to your network toolkits to better manage your net. Please keep in mind that some of these can offer enterprise editions.
Index
- Network management tools
- Net Protocol Analyzers
- Authentication
- Security
- Connectivity
- Filters
- Storage
- Encrypting
- Firewalls and routers
- VPN
- Web Servers
- Servers
- Emulators
- Log Management
- Proxy
- DNS
- For mobiles/Cells
- Queuing
Network management tools
The dude (Linux, Windows y MacOS)
A network tool for self-discovery of any network, graphs the network as a map for easy management. The Dude comprises a client and server. The web control panel is highly useful for network monitoring. The drawback is it doesn’t work to service level.
NetDot (Unix/Linux)
Its main features are:
- Net device discovery using SNMP.
- IPV4 and IPV6 support
- Network address space view
- Help configuring DNS and DHCP
- Network and contact map management, sorted by areas, departments, purveyors, etc.
- Detection and management over network wiring
NMap (Linux/Unix/Windows)
Software meant for auto-discovering network elements and managing their inventories. This tool will allow, apart from discovering servers, finding the services that run on each machine, the OS they’re running them from, and open ports on each machine. It’s also quite useful for security tasks. It is recommended to integrate Nmap with Zenmap (the graphical interface of Nmap)
Nmap is very useful finding vulnerabilities in your network.
Net protocol analyzers (Sniffers)
These network tools are usually used to cleanse tools that use communications via web protocols and to understand what’s happening on a network.
Ntopng (Unix/Linux/Windows)
This tool analyzes net traffic and classifies it. It’s capable of analyzing various different protocols and giving bandwidth and important network metric measurements. The possibility to geolocate machines can be highlighted, though its free version doesn’t offer support on SNMP when consulting SNMP agents.
http://www.ntop.org/products/traffic-analysis/ntop/
Ethereal (Now known as Wireshark)(Unix/Linux/Windows)
One of the best free-distribution network sniffers. It can run on Linux, Unix, and Windows systems. This tool is used to capture any and all traffic that goes through a network interface. Certain additional components need to be added in order to expand on its features. It understands every type of protocol. If there happens to be a protocol that is not supported, the tool allows you to create a plugin so that it may be processed.
One of its star features is the GUI that it offers as well as the capacity to apply filters according to protocol, origin and destiny IP’s, and many others.
More information available here https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireshark.
TCPDump (Unix/Linux/Windows)
We could call this the Ethereal or Wireshark’s offspring. It offers different features but lacks a graphic console. Just like Wireshark, it uses the libpcap library to capture packages.
It can run on Linux and Unix, and for Windows you’ll need to resort to the WinDump version.
Details on TCPDump use can be found on Wikipedia (seriously).
Kismet (Unix/Linux)
A network tool specialized in WiFi traffic. Also, it’s compatible with Wireshark and TCPDump, and allows the possibility to extend its features using a plugin system. It offers the chance to perform a distributed read over network traffic using lightweight clients. On Windows systems, the console will be the only thing that functions, and it’ll need to recover data from a probe installed on a Linux or Unix device.
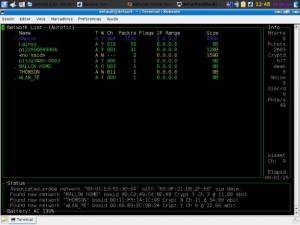
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kismet
Authentication
One of those necessary tools for a network is an authentication system. The most extended protocols for networks are probably RADIUS and LDAP.
FreeRadius (Unix/Linux)
If the protocol you want to use to access networks, websites or other devices is Radius, FreeRadius will be one of your best bets to include this protocol on your networks.
OpenLdap (Unix/Linux)
Used for LDAP directories.
Apache Directory (Unix/Linux/Windows)
LDAP application on the Apache project, with Kerberos 5 compatibility.
Fusion Directory (Linux)
An ideal GUI for managing complex LDAPs. Permits the delegation of non-tech people to access the management of LDAP. Comes with a suite of LDAP admin plugins that round out the initial product.
pGina (Windows)
Authentication system that allows users to be authenticated without the need for an Active Directory. Thanks to pGina it’s possible to integrate Windows user authentication in other free LDAP servers such as OpenLDAP.
Security
DSniff(Unix/Linux)
Network auditing tool. It comes with different tools that can be used to detect vulnerabilities on our network. It can also be used to detect hacker attacks. Furthermore, it analyzes traffic data such as passwords, files, emails, etc.
http://www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff/
Connectivity
eHorus (compatible with any OS – mobile or not – with a browser)
A network tool which provides remote access and management of hardware without the need for installing client applications. From the browser, either from your desktop or cell phone, you can access any network. Free as of 07/12/2016.
VNC (Remote Access tool) (Unix/Linux/Windows)
VNC is one of the simplest yet well known tools used to perform remote access to other devices. What makes VNC special is that it allows the user to export an entire graphic interface from the device we connect to.
It can be used to work with Linux, Unix, Mac OS and Windows.
TeamViewer (Linux/Windows)
A very similar tool to VNC.
OpenSSH (Unix/Linux/Windows)
OpenSSH was basically the first tool available to safely run remote process execution. It allows for SSH and SFTP connections to be established. Also, it allows the user to input remote command lines such as ‘scp’ (secure copy).
The same tool includes an SSH and SFTP client along with its own servers. On Windows this can be used with Cygwin.
Putty (Windows)
The preferred tool to perform remote device access. With this tool which can be easily used and configured, we can access remote devices using the following protocols: Raw, Telnet, SSH, and rlogin. Also, it offers the possibility to create tunnels.
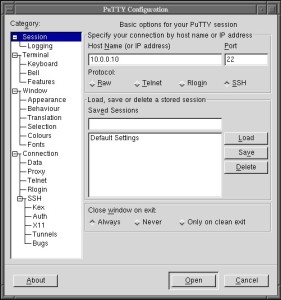
Putty can be easily obtained on the official website.
Filezilla (Unix/Linux/Windows)
One of the most widespread network tools for file management among servers. Totally open and downloadable on https://filezilla-project.org, it also gives users a chance to be installed on an FTP server.
Filters
DansGuardian (Unix /Linux)
Network tool which allows HTTP request filtering according to content. In other words, it’s capable of reading the content on HTTP requests and is able to block out those pages that have undesired keywords, such as sex, viagra, etc. It only runs on Linux and Unix, but upon executing on a server, it can also filter requests that are directed to a Windows operated device.
Storage
FreeNas (Linux)
This is an OS based on FreeBSD that allows the user to configure a server on an online file storage service, in order to share files using the most important protocols: SAI, RSync, Samba, NFS, FTP, SSH, RAID, SMART, etc.
It stands out because of its easy installation and configuration, apart from not needing large servers to properly run.
Encrypting
OpenSSL
Encrypting library that comes with all necessary features to be used. Very useful for generating certificates to implement HTTPS.
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenSSL
Firewalls and Routers
Pfsense (Linux)
This software functions both as a router and a firewall. Indeed it’s a very powerful tool to have in your kit.
The Firewall will allow us to filter according to IP, port and protocol, both in origin and destination. It also allows filtering by Operating System. We may also highlight it’s rule management capabilities and the complements it has to make configurating said rules a lot easier.
One of its largest differences is that it’s focused and statuses and rules that can include statuses to limit a number of requests per second, maximum number of connections to a host, etc.
It also allows configuring a NAT service to establish net package trades between two different networks.
The PFSense suite is quite complete and offers quite a lot of features. Some other distinguished features are: the chance to create VPNs, the possibility to integrate its databases and the RADIUS authentication system, and many more.
Please bear in mind that PFSense offers both a free and an enterprise version.
Shorewall (Linux)
This software comes packed with less features than PFSense, but it’s still quite complete and is totally open. It serves as both a firewall and a router, with quite a few features: Origin and destination IP filtering, Port filters, and protocol filters.
On their site you’ll find documents to help you get the maximum performance from Shorewall. You can also use it as a DHCP, proxy or NAT server, as a bandwidth control system, etc.
VPN
OPENVPN (Windows, Linux, Unix)
An outstanding network tool, which offers Enterprise performance in its open source version. Create your own VPN with secure access. Its main drawback is its lack of compatibility with IPsec.
tinc (Windows, Linux, Unix, iOS)
A network tool based on a Linux daemon which creates VPNs between local Internet hosts. One of its advantages is that it allows a user to create VPNs without the need for installing routers that centralize communications, thanks to Full Mesh Routing.
FreeLan (Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS)
Another alternative for creating VPNs, with a notably powerful configuration.
Web Servers
Apache (Unix/Linux/Windows)
This hyper-famous web server is probably the most used network tool, despite its lack of a management interface. It possesses its own authentication system and the flexibility of its modules and libraries allow an enormously wide array of features.
Koozali SME Server (Unix/Linux/Windows)
Yet another open web server that doesn’t have as much acceptance as Apache, but that is still worth mentioning. Plus, we highlight its features as a mail server, antivirus/antispam, firewall and backup mechanism, among others.
This time it comes with a web management interface.
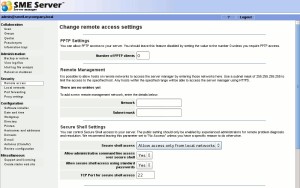
https://wiki.contribs.org/Main_Page
Tomcat (Unix/Linux/Windows)
It stands out from the previous items listed because of the possibility to act as a servlet application container, as well as its capability to run JSP. It can also function solely as a web server.
Servers
FreeSSHd (Windows, Linux y Unix include a default daemon)
An SSH server which has allowing SSH connections as its main function. With this server we will be able to run command lines on a remote console safely.
FreeFTPd (Windows, Linux y Unix include a default daemon)
An FTP server that allows the user to grant FTP access to the device where it has been installed. Apart from (unsafe) FTP connections, this tool allows executing the FTPS and SFTP protocols safely. SFTP allows you to run FTP over TCP/IP for internet connections (using browsers).
OpenSSH
Tool that includes apart from an SSH and SFTP client, a corresponding client for SSH and SFTP servers, in order to give users remote access from other devices.
Emulators
Cygwin (Windows)
Software used on Windows devices and meant for Linux/Unix users. This tool allows a combination of GNU tools which are used on Linux distributions, to be used on Windows. If you want to have a bash console on your Windows, this is the way to go. It’s also quite useful to execute tools that otherwise would not run on Windows since they’re originally compiled for the Linux kernel.
MobaxTerm (Windows)
Graphic console that includes remote execution features using protocols like SSH, FTP, Rlogin, Telnet, RSH, VNC, etc. IT allows the ser to graphically group machines to their correspondent user and password. With X11 it allows exporting the display from a remote Linux/Unix device onto our own Windows PC.
Another very interesting feature is the chance to execute the same command line on multiple terminals. This’ll save us a lot of time when it comes to running configuration deployments, installations or any type of process that requires being executed on multiple devices while maintaining the same procedure.
Furthermore, this tool will allow easy configuration over installed packages to further add extra features.
This software can be found on http://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/
Log Management
Log management and administration is vital for any systems or network administrator. Here’s a list of some of the most useful network tools in this field for log analysis in your infrastructure.
Solr
Although the functions of this software go beyond analyzing logs, it’s still a useful piece of software to know about. It’s supported by large companies who work with applications which need to return searches of huge volumes of data in real time. It can be configured to analyze, integrate and use your applications’ logs.
Graylog2
Open software with an Enterprise version which includes extra functions, capable of processing all your organization’s logs, and configure alerts in function. One of its practical functions is correlating data from different applications in the same thread.
Proxy
Squid (Unix/Linux/Windows)
A proxy server with a caché feature that accelerates and optimizes any network’s communications. It also possesses the possibility to filter traffic, although it’s not as powerful as a dedicated firewall feature.
It’s especially focused on HTTP and HTTPS, but it can also support other protocols.
As additional features we must mention it’s capacity to control net access and traffic limit in order to optimize bandwidth.
DBMail (Linux)
Email storage in relational database. Adapts to any IMAP4 or POP3 client. Stands out for its efficiency in storing and managing emails in its database.
Mailcow (Debian)
A complete mailing suite. Upon installation it automatically deploys and installs useful mail-management software; Postfix, Dovecot, Spamassassin, ClamAV, DKIM, nginx, Apache and/or Roundcube.
Sendmail (Linux, Unix, Windows)
An excellent tool for managing the sending of emails. Its principal function is to route emails sent over different platforms, and it is the most-used MTA system, and one of the most popular network tools. Its chief downside is, it is also one of the most-attacked systems (the price of popularity). However, the Sendmail community is there to deal with threats. Comes with support and an Enterprise version.
hMailServer (Windows)
One of the most popular mail servers, due to its many default functions like an anti-spam system, antivirus, third-party integrations, backup MX, database and administration portal.
DNS
Bind (Linux/Unix)
One of the biggest and best known DNS systems in the open source community. Large ISPs continue to use Bind as a DNS manager and it’s ideal for creating your own DNS in your company. Backed up by a community of users, who make it one of the best network tools for creating DNS servers, whether cache or authoritative. Comes with a complete suite of tools which come in very handy if you work with DNS protocol.
Know (Linux)
Another DNS server but which only fulfills authoritative functions, meaning it only returns DNS replies but without resolving them. Outstanding efficiency.
For mobiles/cells
Mosh (Unix, Linux, Android iOS, macOS)
In the age of mobile communications why not have access to your networked machines while you’re on the go? Mosh provides the same functions as shells like Putty but adapted for mobile devices.
Queuing
Queue systems are indispensable to manage communications in complex infrastructures where there are many applications all communicating with one another in different languages. Due to the complex middleware area of many large companies, this list also includes a few MQ message systems worth knowing and recommended to ad in your network tools kit set.
RabbitMQ
Recently, one of the most popular MQ message systems, even displacing IBM’s MQ in some organizations. Maintained currently by VMWare.
Apache Kafka
An Open alternative to the above; similar functions, but with performance depending on what the user proposes. This article contains some interesting observations about the two systems, and their principal differences. https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-differences-between-Apache-Kafka-and-RabbitMQ
We hope this list of network tools is useful and that way you’re able to manage your network in the best way possible. If you know of any tool that’d deserve to be here, don’t hesitate to comment!!
Pandora FMS’s editorial team is made up of a group of writers and IT professionals with one thing in common: their passion for computer system monitoring. Pandora FMS’s editorial team is made up of a group of writers and IT professionals with one thing in common: their passion for computer system monitoring.