What is RAID? What types of RAID are out there?
What is raid? Do you want to find out?
The term RAID is related mostly to those components of our computers that allow us to store information and get our computer up and running properly.. What would we do without hard drives? Well…
In this article we are going to learn what a RAID is and some of the types of RAID that exist. Let’s go!
What is RAID?
As you may guess, RAID is an acronym, which stands for “Redundant Set of Independent Disks”.
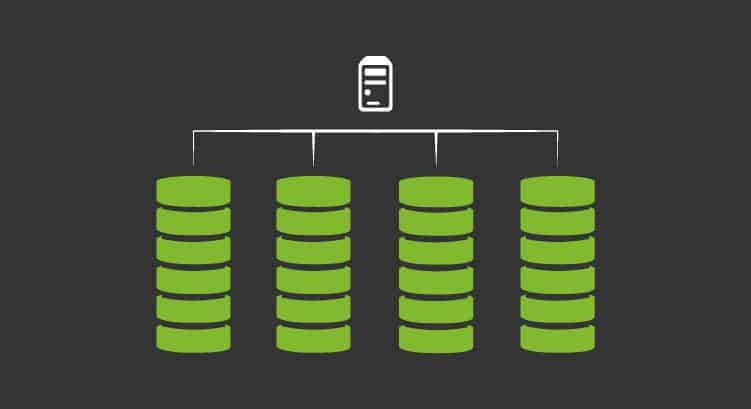
RAID refers to a type of configuration that uses multiple hard disks that work in a coordinated manner in order to achieve various benefits related to key factors such as storage volume or data availability.
The area in which RAID configurations are most often used is the enterprise, or those entities that need to store a large amount of data and have high availability, safe from errors or losses. So it would be strange if your grandmother had set up a RAID configuration on her computer in her old house.
Some benefits of RAID configuration
As we said, RAID configuration usually seeks various effects.
On the one hand, the use of several hard disks, allows an increase in the volume of data that we are able to store.
On the other hand – and this is one of the most frequently sought-after benefits – the use of various disks facilitates data retention and fault tolerance through duplication. For example, it is very common to use RAID configuration on servers, in order to maintain service availability even if one of the hard disks breaks down.
But there’s more. We can also use the RAID configuration to obtain other advantages, such as an increase in the speed of the hard disks.
One thing to keep in mind is that there is not just one type of RAID configuration, but several, and that depending on the chosen one we will get some benefits. Let’s look at some examples.
What is RAID? Some types of RAID
As we said, the benefits of RAID configurations have a lot to do with the type of configuration we use. These are some of the most common RAID classes.
–RAID 0: Class 0, also called striping, differs from others in that it does not seek data redundancy, but rather distributes information between different hard disks.
Thus, this type of configuration seeks to achieve an increase in speed. With this type of configuration we will not be keeping an extra copy of our data, which will have to be taken into account when dealing with faults or breakdowns, which could lead to partial or total loss of information. This is a configuration that is often used in activities that demand a high rate of bandwidth transfer, such as video editing, and where data integrity is not the most important thing.
–RAID 1: Known as “mirroring” what it looks for is, precisely, to turn a hard disk into the “mirror” or copy of another.
This is the classic configuration when what we want is to avoid the loss of our data. The duplication of information offered by mirroring seeks to maintain data integrity and guarantee service in cases where one of the two hard disks may fail.
Due to its characteristics, it is widely used in areas that demand data security and availability, such as business activity.
–RAID 5: It is known by a somewhat more complex term than the previous ones: distributed by parity. In this type of configuration the information is divided into blocks that are distributed by the different hard disks. At the same time, a “parity block” is created that would allow us to reconstruct the information in the event that one of the hard disks breaks down.
Due to its characteristics, it is a configuration widely used in different types of servers.
–RAID 0+1: Its name says it all; it is an option that combines RAID 0 configuration with RAID 1. Thus, 2 pairs of hard disks are formed in which the information is divided (RAID 0) and at the same time duplicated (RAID 1), so you get the two benefits of these types of configurations (higher speed and duplication of data).
–RAID 10: Also known as RAID 1+0, in this case what we do is a mirror for each disk that is working in stripping. It is widely used in database servers and is one of the most commonly used configuration types, as its fault tolerance is considered to be greater than that of RAID 0+1.
Now, these are not the only RAID configuration options. In fact, there are considered to be at least 10 different configurations in RAID. It’s a matter of thinking through the type of configuration that will best suit your needs and taking into account the means at your disposal.
And now… It’s time to monitor!
What is RAID? Now that we know this, and some of the different types of RAID, how about spending a few minutes to know Pandora FMS?
Pandora FMS is a flexible monitoring software, capable of monitoring devices, infrastructures, applications, services and business processes.
Do you want to know what Pandora FMS can offer you? Click here.
Or you can also send us any query you may have about Pandora FMS. You can do it in a very simple way, thanks to the contact form that can be found here.
Our Pandora FMS team will be happy to assist you!
Pandora FMS’s editorial team is made up of a group of writers and IT professionals with one thing in common: their passion for computer system monitoring. Pandora FMS’s editorial team is made up of a group of writers and IT professionals with one thing in common: their passion for computer system monitoring.