Distributed monitoring with Satellite server
Introduction
The Satellite Server is used to discover and monitor remote networks and equipment, either network elements (routers, switches, etc.) through SNMP or ICMP, or MS Windows® (via WMI) or GNU/Linux® (via SNMP) servers. It is particularly useful to monitor remote networks that are not accessible from Pandora FMS server, and where Software Agents cannot be installed either.
The Satellite Server has some features that make it special:
- It can run network tests (ICMP, Latency and SNMP v1 and v2) at an extremely high rate (500 checks per second). For SNMP v3, configure login credentials and due to data encryption, it will do slower checks.
- It only sends data to the server every N seconds (by default 300), but it can run latency, ICMP and SNMP tests with a shorter interval so that, when it detects status changes, it immediately notifies the server. These status changes have to be previously defined if the Module type is not
*_proc(e.g. network interfaces or general network connectivity). - It is a standalone server, it does not require connection to Pandora FMS database. It sends all data as XML, so that it works as an independent server, similar to a Software Agent in broker mode or to an Export Server.
- It has an autodiscovery mechanism for SNMP and WMI, so it creates detected Agents (by IP address), as well as dynamic elements (network interfaces, storage) and monitors them automatically.
- On MS Windows® systems, it detects disks, CPU and memory.
- In network systems with SNMP, it detects interface status, incoming and outgoing traffic per interface, and the system name.
- Auto-generated Modules may be modified as another module, managing the Agent from the console, as if it were an ordinary Agent (in the Massive Operations → Satellite section).
- Agents may be created manually by generating an Agent configuration file in the Satellite Server configuration directory.
- Both the Satellite server and the Network Server support IPv6 in all its advanced features.
Installation
Online installation tool
Please contact the sales team, ask for a quote or ask your questions about licenses at this link.
This tool supports Rocky Linux 8.x, AlmaLinux 8.x and RHEL 8.x .
Requirements for the use of the online installation tool:
- Have access to the Internet.
- Have curl installed (it comes by default in most distributions).
- Comply with the minimum hardware requirements.
- Be an administrator user root.
- Have a supported OS.
- In the case of using RHEL 8, it will be necessary to activate it previously with a license and be subscribed to standard repositories.
To use the online installation tool, just access the command line provided by your Cloud provider, with root admin user, and run:
export PANDORA_SERVER_IP='<PandoraServer IP or FQDN>' && curl -Ls https://pfms.me/satellite-ent-deploy| bash
Custom installation using the online installation tool:
PANDORA_SERVER_IP: IP address or FQDN of Pandora FMS server to which the Satellite server will point. Mandatory parameter.TZ: Satellite server time zone. Optional parameter.SATELLITE_SERVER_PACKAGE: Custom URL of Satellite server installation tarball package. Optional parameter.SATELLITE_KEY: Satellite server license for automatic activation. Optional parameter.REMOTE_CONFIG: Remote configuration. Optional parameter, enabled by default (value1).INSTALL_AGENT: Optional parameter, enabled by default (value1). It allows installing the Software Agent (all configuration variables of the online agent installer).VMWARE_DEPENDENCIES: Optional, it allows to install VMware® plugin dependencies, disabled by default (0).ORACLE_DEPENDENCIES: Optional, it allows to install dependencies of the Oracle® plugin, disabled by default (0).MSSQL_DEPENDENCIES: Optional, it allows you to install MS SQL Server® plugin dependencies, disabled by default (0).SKIP_KERNEL_OPTIMIZATIONS: Disable the recommended kernel optimization, advanced, disabled by default (0).
env TZ='Europe/Madrid' \ SATELLITE_KEY='SOPORTEDEV00RS0REB3M2T7ZHISO51IIQH52JISJ47VGHIRM...'\ PANDORA_SERVER_IP='192.168.10.10' \ REMOTE_CONFIG=1 \ INSTALL_AGENT=1 \ VMWARE_DEPENDENCIES=1 \ ORACLE_DEPENDENCIES=1 \ MSSQL_DEPENDENCIES=1 \ SKIP_KERNEL_OPTIMIZATIONS=0 \ sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://pfms.me/satellite-ent-deploy)"
Satellite Server installation on GNU/Linux
The recommended GNU/Linux operating system is RedHat Enterprise -RHEL- 8 / Rocky Linux 8 (EL8) and it supports EL9.
Install Fping, Nmap and libnsl separately and first configure the EPEL repository. Visit the following link:
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/epel/#_quickstart
and select the operating system. If Rocky Linux 8 is used:
dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools dnf install epel-release
Install Perl with the following command:
dnf install perl
Satellite Server core dependencies: PandoraWMIC (version 762 and later), Fping, Nmap and libnsl. Braa and PandoraWMIC dependencies are attached to the installer.
dnf install fping nmap libnsl
Once you download the package containing the Satellite Server, go to the download folder with root privileges and unzip the binary:
tar -xvzf pandorafms_satellite_server_X.XNG.XXX_x86_64.tar.gz
A folder named satellite_server will be generated. Go to this folder by typing:
cd satellite_server/
To install the Satellite Server itself, run the install command:
./satellite_server_installer --install
Once the process is finished, edit the Satellite configuration file located at:
/etc/pandora/satellite_server.conf
Search for the token server_ip and enter the IP address or domain of Pandora FMS server to which the Satellite server will connect.
After that, you may save the file and start the service by running the following:
sudo systemctl start satellite_serverd
In case of any error or malfunction, check the log file at:
/var/log/satellite_server.log
Installation on MS Windows
Pandora FMS Satellite server needs WinPcap and Visual Studio 2010 SP1 (both included in the installer) to work properly.
With administrator rights, run the digitally signed installer (version 762 and later). The installation window will appear in the next step of the installation.
Then enter Pandora FMS license key to continue with the installation.
Please contact the sales team, ask for a quotation or ask your questions about licenses at this link.
In the following section, configure Pandora FMS server address to send data; you may define the network exploration rules for the Satellite Server. It will be necessary to restart the machine for all the changes to be applied.
Once the process is complete, you may start and stop the Satellite Server PFMS service from the MS Windows® Start menu.
Operation of WMI Modules in some MS Windows versions
For MS Windows® security reasons, some versions have limited users to perform remote WMI queries. In case these queries are not performed, the solution is to run the Satellite Server service as Administrator user.
Open services:
Click on the service and enter Properties:
On the Login window, select an account with Administrator permissions and apply the changes:
The service must be restarted to apply the changes.
Configuration
All parameters that require a timeout or expiration time must be specified in seconds (by default 300 seconds, i.e., 5 minutes).
Unless otherwise stated, each token must appear only once in each configuration file.
It is important to note that the latency and SNMP intervals are specific to the state change:
- In the case of Boolean checks (port state, machine state), the threshold defining the state change is automatic.
- In the case of numeric values (latency, network traffic on an interface, disk space, CPU, etc.), it is based on the threshold.
- By default no thresholds are defined; this has to be done in Module definition.
agent_interval
agent_interval xxx
By default, 300 seconds (5 minutes). This will be the time after which data will be sent to the server, regardless of whether the checks made by the Satellite Server have a shorter interval. If necessary, and by default, Agents are created in the corresponding Pandora FMS server, according to the time specified here.
If the collected data changes compared to the previous one, it sends it at that moment. If it is the same, it will send it when the interval of that Agent orders it. It is useful to perform very intensive tests and to notify only in the case of a state change.
agent_threads
agent_threads xxx
Number of threads used to send XML data files.
log_file
log_file <path_file>
It specifies the file where the Satellite Server log is written, by default /var/log/satellite_server.log.
recon_task
recon_task xxxxx[,yyyy]
IP addresses/networks used for Autodiscovery, separated by commas. For example:
192.168.50.0/24,10.0.1.0/22,192.168.70.64/26
server_ip
server_ip <IP>
IP address or DNS name of Pandora FMS server to send the information to. The data is sent by Tentacle, so the communication towards the server should be allowed and guaranteed by port 41121/tcp.
recon_mode
recon_mode <mode_discovery>
Auto-discovery mode ( < mode_discovery > ) to be used. The system will employ the following protocols to discover systems:
recon_mode icmpIt performs checks to determine whether the host is online (ping) and measures latency time.recon_mode snmpIf it is able to communicate through SNMP (v1 and v2 only), it will search for all network interfaces and pull traffic from all of them, as well as their operational status, device name and location. It will try with the different communities supplied in the configuration file to connect. For using SNMP v3, whose recognition is unnecessary, see this link on how to configure the known access credentials.recon_mode wmiSimilar to the previous case, in this case showing CPU, Memory and Disk Load (all available).
recon_community
recon_community <aaa>,<bbb>,<ccc> …
It specifies a comma-separated list of SNMP communities < xxx > for use in SNMP Discovery. It will use this list in SNMP scanning: for each IP address found, it will try to see if it responds to any of these communities.
wmi_auth
wmi_auth Administrator%password[,user%pass]
It specifies a list of pairs of user credentials, each in this separated commas format:
< username >%< password >
wmi_ntlmv2
wmi_ntlmv2 [0|1]
It enables 1 or disables 0 authentication with the NTLMv2 protocol for WMI.
agent_conf_dir
agent_conf_dir <path>
Path ( < path >) to the directory that automatically creates and stores the configuration files of each Agent created by the Satellite Server. By default /etc/pandora/conf. These Agents can also be manually created.
group
group <group_name>
It defines the default group name < group_name > of the Agents created by the Satellite Server.
daemon
daemon [1|0]
If its value is 1, it runs the daemon (service) in the background (default value).
host_file
host_file <path_filename>
It is an alternative or complementary method to scanning a network to find hosts.
In this file ( < path_filename > ), in each line there is an address. Alternatively, you may type in the same line the hostname followed by the IP address, so that the Agent will be created with that name and also use that IP address for the Modules. It is necessary that when performing a query with fping to these addresses, the result must match for these addresses to be valid.
pandora_license_key
Version 765 or later.
# Encryption key for the Pandora FMS license. # pandora_license_key
For safe transmission of the license to the Satellite server, you should configure in the Web Console or in the Command Center (Metaconsole) the same encryption key that you will enter in this token.
See also token server_ip .
remote_config
remote_config [1|0]
It enables by default the remote configuration in the detected Agents, necessary if you want to manage them from the Console after detecting them. It also enables the remote configuration of the Satellite Server itself.
temporal_min_size
temporal_min_size xxx
If the free space (in megabytes) of the partition where the temporary directory is located is less than this value, no data packets are still generated. This prevents the disk from filling up if for some reason the connection to the server is lost for an extended period of time.
xml_buffer
xml_buffer [0|1]
Default value 0. Being configured with value 1, the Agent will save the XML data that it has not been able to send to try again later.
On Unix, if you are in a safe environment consider changing the temporary directory, as /tmp has write permissions for all users.
snmp_version
snmp_version xx
SNMP version to be used, by default 1. To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
Some Modules may stop working if this value is changed.
braa
braa <path>
< path > to the Braa binary. Default value /usr/bin/braa.
fping
fping <path>
< path > to the Fping binary. Default value /usr/sbin/fping.
fsnmp
fsnmp <path>
< path > to the Fsnmp binary (SNMPv3). Default value /usr/bin/pandorafsnmp.
latency_packets
latency_packets xxx
Number of ICMP xxx packets sent per latency request.
nmap
nmap <path>
< path > to the Nmap binary. Default value /usr/bin/nmap.
nmap_timing_template
nmap_timing_template x
An x value specifying the level of aggressiveness of Nmap, from 1 to 5. One means slower but more reliable, five means faster but less reliable. Default value: 2.
ping_packets
ping_packets xxx
Number of ICMP packets sent per ping.
recon_enabled
recon_enabled [0|1]
It enables (1) or disables (0) the equipment autodiscovery.
recon_timing_template
server_port
server_name
server_name xxxxx
Name of the Satellite server (by default it takes the hostname of the machine).
server_path
server_path <path>
< path >' where XML files are copied if the transfer_mode is set to local (default /var/spool/pandora/data_in).
server_opts
Server parameters that are passed to Tentacle.
transfer_mode
transfer_mode [tentacle|local]
File transfer mode. It can be only tentacle or local (default tentacle).
snmp_verify
snmp_verify [0|1]
It enables (1) or disables (0) the checking of SNMP v1 modules that cause Braa to fail in real time. These Modules will be discarded and will stop running. See also both snmp2_verify and snmp3_verify.
snmp2_verify
snmp2_verify [0|1]
It enables (1) or disables (0) the checking of SNMP v2 modules that cause Braa to fail in real time. These modules will be discarded and will stop running. See also both snmp_verify and snmp3_verify.
Testing SNMP version 2 modules can be very slow.
snmp3_verify
snmp3_verify [0|1]
It enables (1) or disables (0) the checking of SNMPv3 modules that cause Braa to fail in real time. These modules will be discarded and will stop running. See also both snmp_verify and snmp2_verify.
To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
snmp3_seclevel
Security level used for SNMPv3 messages (noauth, authnopriv or authpriv).
To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
snmp3_secname
Security name used for SNMPv3 messages.
To use SNMP v3 see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
snmp3_authproto
Authentication protocol (md5 or sha) for authenticated SNMPv3 requests.
To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
snmp3_authpass
Authentication password for authenticated SNMPv3 request.
To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
snmp3_privproto
Privacy protocol (des or aes) for encrypted SNMPv3 requests.
To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
snmp3_privpass
Privacy password for encrypted SNMPv3 messages.
To use SNMP v3, see in this link how to configure the known access credentials.
startup_delay
startup_delay xxx
Wait xxx seconds before sending data files for the first time.
temporal
temporal <directory>
Temporary directory where XML files are created, by default /tmp.
tentacle_client
tentacle_client <path>
< path > of the Tentacle client. Default value /usr/bin/tentacle_client.
wmi_client
wmi_client <path>
< path > to the wmi_client binary. Default value /usr/bin/wmic.
snmp_blacklist
snmp_blacklist <path>
< path > to the SNMP Module exclusion list. Default value /etc/pandora/satellite_server.blacklist.
add_host
add_host <IP_addr> [ agent_name ]
Adds the given host ( [ agent_name ] ) to the list of monitored agents. You may specify the Agent name after the IP address ( < IP_addr > ). Multiple hosts can be added, one on each line separately.
ignore_host
ignore_host <agent_name>
It removes the given host from the list of monitored Agents, even if it is found in a network scan by a Recon Task. The host must be identified by the Agent name. Multiple hosts can be ignored, one per line.
delete_host
delete_host <agent_name>
It removes the given host from the list of monitored Agents permanently by deleting its configuration file. The host must be identified by the Agent name < agent_name >. Multiple hosts can be deleted, one per line.
keepalive
keepalive xxx
The Satellite Server reports its status and checks for changes in the remote configuration (of the Agents and itself) every xxx seconds. Default value: 30 seconds.
credential_pass
credential_pass xxx
Password used to encrypt the passwords of the credential boxes. It should be the same as the one defined in Pandora FMS Console. By default the host name is used.
timeout_bin
timeout_bin <path>
If defined, the timeout program (usually /usr/bin/timeout) will be used when calling the Tentacle client.
timeout_seconds
timeout_seconds xxx
Timeout time, in seconds, for the timeout program. The timeout_bin parameter must be set.
proxy_traps_to
proxy_traps_to <dir_IP[:port]>
It redirects SNMP traps received by the Satellite Server to the address (and port, optionally) specified. By default port 162 is used.
proxy_tentacle_from
proxy_tentacle_from <dir_IP[:port]>
It redirects data received by Tentacle server from the address (and port, optionally) specified. By default, port 41121 is used.
proxy_tentacle_to
proxy_tentacle_to <dir_IP[:port]>
It redirects Tentacle client requests received by the Satellite Server to the address (and port, optionally) specified. By default, port 41121 is used.
This option may be in conflict with remote configuration of agents. This happens should you intend to use the Satellite Server as a proxy for some Software Agents and monitor them remotely from the Satellite Server itself (ICMP, SNMP, etc.) with remote configuration enabled in both cases. In this situation you should either use different Agents for the checks made (i.e. with different agent_name), or leave the remote configuration enabled only in one of the two (Satellite Server or Software Agents).
dynamic_inc
dynamic_inc [0|1]
With a value of 1, it moves automatically discovered dynamic modules (SNMP, WMI,…) to separate files so that they do not interfere with remote configuration of Agents.
vlan_cache_enabled
vlan_cache_enabled [0|1]
It enables (1) or disables (0) the VLAN cache of auto-discovered hosts.
verbosity
verbosity <0-10>
Level of detail in the log record, where 10 is the most detailed level of information.
agents_blacklist_icmp
agents_blacklist_icmp 10.0.0.0/24[,8.8.8.8/30]
ICMP check exclusion list. This field can be configured with a list of IP addresses using CIDR notation to prevent ICMP type modules from being executed. Multiple subnets can be specified by separating them by commas.
agents_blacklist_snmp
agents_blacklist_snmp 10.0.0.0/24[,8.8.8.8/30]
SNMP check exclusion list. This field can be configured with a list of IP addresses using the CIDR notation to prevent SNMP modules from running. Multiple subnets can be specified by separating them by commas.
agents_blacklist_wmi
agents_blacklist_wmi 10.0.0.0/24[,8.8.8.8/30]
WMI check exclusion list. This field can be configured with a list of IP addresses using CIDR notation to prevent WMI modules from running. Multiple subnets can be specified by separating them by commas.
general_gis_exec
general_gis_exec xxx
Enabling this option will use a script to provide GIS positioning to all Agents detected by the Satellite Server. The script must have execution permissions and display the coordinates in format <longitude>,<latitude>,[<altitude>] The third parameter, the altitude, is optional.
forced_add
force_add [0|1]
If set to 1, hosts added manually (via host_file or add_host) will always be created, even if they do not respond to ping, with a configuration file without modules.
agent_block
conf_interval
conf_interval XXX
Remote configuration check interval, by default 300 seconds.
exec_interval
exec_interval XXX
Time between execution checks, by default 300 seconds.
exec_threads
exec_threads X
Number of threads used for module execution, 5 by default. It will depend on the power (CPU and RAM) of the machine. The more threads, the more the system will be loaded, but the more processing capacity it will have. When exceeding 20 threads, depending on the system, performance may become poor.
latency_block
latency_block XXX
Number of hosts processed in a single call to nmap (latency), by default 400.
The higher the number (maximum 500), the more processing capacity you will have, but at the cost of increased latency. In some cases it may be convenient to reduce this number.
latency_interval
latency_interval XXX
Time between latency checks, by default 180 seconds.
latency_retries
latency_retries X
Number of retries for latency modules, by default 2 attempts.
latency_threads
latency_threads X
Number of threads used for the latency check, by default 4 threads.
latency_timeout
latency_timeout X
Timeout for latency checks in seconds, by default 1.
ping_block
ping_block XXX
Number of hosts processed in a single nmap (ping) call, by default 400.
The higher the number (maximum 500), the more processing capacity you will have, but at the cost of increased latency. In some cases it may be convenient to reduce this number.
ping_interval
ping_interval XXX
Time between ping checks, 120 seconds by default.
ping_retries
ping_retries X
Number of retries for latency modules, 2 by default.
ping_threads
ping_threads X
Number of threads used for ping checks, 4 by default.
ping_timeout
ping_timeout X
Timeout for ping checks in seconds, by default 1.
plugin_interval
plugin_interval XXX
Time between plugin checks, by default 300 seconds.
plugin_threads
plugin_threads X
Number of threads used for plugin testing, by default 2 threads.
plugin_timeout
plugin_timeout XX
Timeout for plugin checks in seconds, by default 10 seconds.
recon_interval
recon_interval XXXXXX
Time between network scans in seconds, by default 604800 seconds.
snmp2_block
snmp2_block XX
Number of hosts processed in a single call to Braa (SNMPv2c), 50 by default.
snmp2_interval
snmp2_interval XXX
Time between SNMP checks (SNMPv2c), by default 180 seconds.
snmp2_retries
snmp2_retries X
Number of retries for SNMP modules (SNMPv2c), by default 2 retries.
snmp2_threads
snmp2_threads X
Number of threads used for SNMP checks (SNMPv2c), by default 8 threads.
snmp2_timeout
snmp2_timeout X
Timeout for SNMP checks (SNMPv2c) in seconds, by default 5.
snmp3_block
snmp3_block XX
Number of hosts processed in a single call to Braa (SNMPv3), 50 by default.
snmp3_interval
snmp3_interval XXX
Time between SNMP checks (SNMPv3), by default 180 seconds.
snmp3_retries
snmp3_retries X
Number of retries for SNMP modules (SNMPv3), by default 2 retries.
snmp3_threads
snmp3_threads X
Number of threads used for SNMP checks (SNMPv3), by default 4 threads.
snmp3_timeout
snmp3_timeout X
Timeout for SNMP checks (SNMPv3) in seconds, by default 5 seconds.
snmp_block
snmp_block XX
Number of hosts processed in a single call to Braa (SNMPv1), by default 50.
snmp_interval
snmp_interval XXX
Time between SNMP checks (SNMPv1), by default 180 seconds.
snmp_retries
snmp_retries X
Number of retries for SNMP modules (SNMPv1), 2 by default.
ssh_interval
ssh_interval XXX
Time between SSH checks, by default 300 seconds.
ssh_threads
ssh_threads XXX
Number of threads used for SSH modules, by default 5 threads.
ssh_timeout
ssh_timeout X
Timeout for SSH checks in seconds, by default 2 seconds.
tcp_interval
tcp_interval XXX
Time between TCP checks, by default 300 seconds.
tcp_threads
tcp_threads X
Threads dedicated to TCP checks, by default 5 threads.
tcp_timeout
tcp_timeout X
Timeout for TCP checks, by default 1 second.
snmp_threads
snmp_threads X
Number of threads used for SNMP checks (SNMPv1), by default 8 threads.
snmp_timeout
snmp_timeout X
Timeout for SNMP checks in seconds (SNMPv1), by default 5 seconds.
wmi_interval
wmi_interval XXX
Time between WMI checks, by default 300 seconds.
wmi_threads
wmi_threads X
Threads dedicated to WMI polling, by default 5 threads.
ipam_task
ipam_task <id IPAM TASK> , <CIDR>
Comma-separated list of networks (in SLASH notation) to be scanned by IPAM. They must be preceded by the IPAM task identifier assigned in PFMS when created (the Discovery server field must be left unassigned to be assigned later to a Satellite server). For example: 1,192.168.0.0/24.
ipam_interval
ipam_interval XXXXXX
Time between scanning tasks in seconds.
wmi_credential_encrypt
It enables or disables WMI module password encryption (module_wmiauth) and in the global wmi_auth token. If there is no credential_pass the Satellite server name is used for encryption. Values: 1 or 0, by default 0.
snmp3_credential_encrypt
It enables or disables SNMPv3 module password encryption (module_authpass and module_privpass) and in global tokens snmp3_authpass and snmp3_privpass. If there is no credential_pass, the Satellite server name is used for encryption. Values: 1 or 0, by default 0.
ssh_credential_box
That token is the same as using credential_box. A new name is given to distinguish it from the new credential boxes added for WMI and SNMPv3 modules.
This command may take up multiple lines with different configurations.
wmi_credential_box
It works similarly to credential_box and it is specific for WMI modules.
If a WMI module has no credentials and its IP address matches the network indicated by a WMI credential box, will use it, otherwise, it sill use wmi_auth global configuration.
This command may take up multiple lines with different configurations.
snmp3_credential_box
It works similarly to credential_box and it is specific for SNMPv3 modules.
If a SNMPv3 module has no credentials (authpass, module_authpass, privpass, module_privpass) and its IP address matches the network indicated by an SNMPv3 credential box, it will use. Otherwise it will use the global snmp3_authpass or snmp3_privpass cofniguration.
This command may take up multiple lines with different configurations.
Secondary Server
secondary_mode [on_error|always]
A special type of general configuration parameter is the definition of a secondary server. This allows you to define a server to which data is sent, in addition to the server defined by default. The secondary server mode works in two ways:
- on_error: It sends data to the secondary server, only if it cannot send it to the primary server.
- always: It always sends data to the secondary server, regardless of whether or not it can contact the primary server.
secondary_server_ip 192.168.1.123 secondary_server_path /var/spool/pandora/data_in secondary_mode on_error secondary_transfer_mode tentacle secondary_server_port 41121
Remote configuration
Remote file configuration
The advanced editor for remote configuration of the Satellite server can be accessed on PFMS server to which the Satellite server belongs through the menu Management → Servers → Manage servers. Once the page has loaded in the web browser, click on the Remote configuration icon.
Then click on the Advanced editor icon:
In the text box corresponding to Configuration, you will be able to edit and/or add each of the tokens described in previous sections. When finished editing, save the changes by clicking Update located at the bottom of the page.
The synchronization and loading of the new tokens will take some time. Please allow a few moments for the changes to propagate.
Remote configuration graphical interface
Version NG 764 or later.
The graphical interface on PFMS server to which the Satellite server belongs can be accessed remotely through the Management → Servers → Manage servers menu and then clicking on the Remote configuration icon.
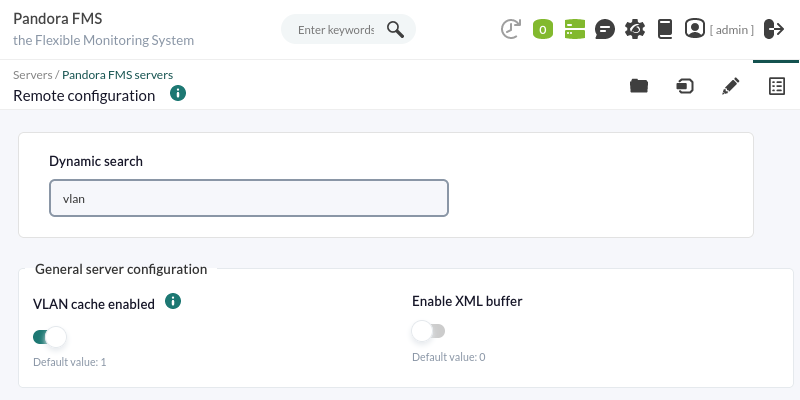
By default the following standard configuration is displayed (on the left tab is the advanced configuration).
Use dynamic search to enter key text (one letter or more) and search for a specific token.
Some tokens only accept two values (ON / OFF), the first button is used to change this value. If you enable or disable the corresponding token with the second button, the Satellite server will take the default value assigned to it (1 or 0) regardless of the value set by the first button.
Once you make all the changes, click Update to save the preferences.
Agent Creation in Satellite Server
There are three ways to create the Agents in the Satellite Server: Recon Task, satellite_hosts.txt file or manually by creating the .conf files of the Agents to be monitored.
Agent Creation through Recon Task
Agent creation through a Recon Task is the most used by Pandora FMS users. To carry it out, access the Satellite Server configuration file and configure the following parameters:
- recon_community: A comma-separated list of SNMP communities for use in SNMP Discovery must be specified (in the case of performing an SNMP Recon Task).
- recon_enabled: It must be set to
1to enable the Satellite Server's Recon Task. - recon_interval: Time interval where the network is scanned, in seconds (default
604800seconds,7days). - recon_mode: Mode of Recon Task (SNMP, ICMP, WMI), separated by commas.
- recon_task: List of networks to be surveyed, separated by commas.
- recon_timing_template: A value specifying how aggressive nmap will be, from 1 to 5. One means slower but more reliable; five means faster but less reliable (default 3).
An example of a Recon Task realization is:
recon_community public recon_enabled 1 recon_interval 604800 recon_mode icmp,snmp,wmi recon_task 192.168.0.0/24,192.168.1.0/24 recon_timing_template 3
Once the data has been configured, the Satellite Server is run using the command:
systemctl start satellite_serverd
Agents whose configuration files do not contain any Modules will be ignored by the Satellite Server.
Agent configuration by file
First of all, in order to create an Agent using the satellite_hosts.txt file, go to the Satellite Server configuration file and remove the comment line:
host_file /etc/pandora/satellite_hosts.txt
Secondly, the file must be created in the path indicated above with the IP addresses of the hosts to be created by entering the IP address and name of the Agent:
192.168.10.5 Server5 192.168.10.6 Server6 192.168.10.7 Server7
In order for Agents with these IP addresses to be created, they must respond to the fping call, otherwise they will not be created.
Once the data has been configured, the Satellite Server is started with the command:
systemctl start satellite_serverd
The indicated file is read every recon_interval seconds.
Manual agent creation
In the directory /etc/pandora/conf (by default) the configuration files of the new Agents are stored. Open a terminal window and go to this folder:
cd /etc/pandora/conf
Then proceed to create a file with a .conf extension, for example “file.conf”. The following fields must be filled in manually:
- agent_name: Name to be assigned to the Agent.
- agent_alias: Alias to be assigned to the Agent.
- address: IP address of the element to be monitored.
- group: Group to which to assign the Agent.
- gis_exec: Positioning script (optional). If used, it overwrites the location provided by the general_gis_exec parameter of the Satellite Server.
- The Modules to be created in the Agent are added.
An example would be:
agent_name Example agent_alias This is an example address 127.0.0.1 group Servers module_begin module_name Ping module_ping module_end module_begin module_name Latency module_latency module_end
Once the data has been configured, the Satellite Server is started with the command:
systemctl start satellite_serverd
Agent removal in Satellite Server
A total Agent deletion or a partial Agent deletion can be performed.
First make a backup of all folders and their files before proceeding.
For total Agent deletion, the method used in Agent creation must be taken into account:
- Manual: First of all, the
.conffiles of the Agents created in the/etc/pandora/conffolder must be deleted and then Agents must be deleted in the console. - File
satellite_hosts.txt: The file will have to be deleted, as well as the.conffiles that have been created in the/etc/pandora/conffolder, and then delete the Agents in the Console. - Recon_task: It will be necessary to deconfigure the
recon_taskin the.conffile of the Satellite Server, delete the.confthat have been created in the/etc/pandora/conffolder and then delete the Agents in the Console.
For partial deletion, the method used in the creation of Agents must also be taken into account.
- Manual: First of all, the
.conffiles of the Agents to be deleted in the/etc/pandora/conffolder must be deleted and then the Agents must be deleted in the console. - File
satellite_hosts.txt: It will be necessary to delete from the file, the lines of the IP addresses to be deleted, as well as the.confthat have been created in the folder/etc/pandora/confwith those IP addresses, and then delete the Agents in the console. - Recon_task: You will have to configure the
recon_taskexcluded list in the.conffile of the Satellite Server, then delete the.confthat have been created in the/etc/pandora/conffolder with those IP addresses and delete the Agents in the console.
Customized configurations per Agent
In addition to “automatic” Modules, any TCP, SNMP, WMI or SSH check that is available can be added to the monitoring, using a syntax similar to the one used for local Modules in Software Agents. Some examples of valid Modules for the Satellite Server are exposed, as they are autogenerated after detecting the system.
ICMP/TCP queries
Connectivity to a machine (through PING):
module_begin module_name ping module_type generic_data module_ping 192.168.70.225 module_end
Checking a port (through TCP):
module_begin module_name Port 80 module_type generic_proc module_tcp module_port 80 module_end
WMI Queries
WMI query for CPU usage (percentage):
module_begin module_name CPU module_type generic_data module_wmicpu 192.168.30.3 module_wmiauth admin%none module_end
WMI query for free memory (percentage):
module_begin module_name FreeMemory module_type generic_data module_wmimem 192.168.30.3 module_wmiauth admin%none module_end
Generic WMI query:
module_begin module_name GenericWMI module_type generic_data_string module_wmi 192.168.30.3 module_wmiquery SELECT Name FROM Win32_ComputerSystem module_wmiauth admin%none module_end
See also credential encryption with wmi_credential_box token.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 queries
Make sure that the OIDs begin with a dot or the SNMP modules will not work!
Interface status through SNMP. The Satellite Server automatically detects each interface:
module_begin module_name if eth1 OperStatus module_description IP address N/A. Description: The current operational state of the interface. The testing(3) state indicates that no operational packets can be passed. module_type generic_data_string module_snmp 192.168.70.225 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8.3 module_community artica06 module_end
To force the module to use SNMP version 2c, the following line is added:
module_version 2c
To force the module to use SNMP version 1, the following line is added:
module_version 1
For example:
module_begin module_name if eth1 OperStatus module_description IP address N/A. Description: The current operational state of the interface. The testing(3) state indicates that no operational packets can be passed. module_type generic_data_string module_snmp 192.168.70.225 module_version 2c module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8.3 module_community artica06 module_end
Generic SNMP query. In this case the Satellite Server automatically retrieves the traffic from each interface, with its “real” descriptive name:
module_begin module_name if eth0 OutOctets module_description The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing characters. module_type generic_data_inc module_snmp 192.168.70.225 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16.2 module_community public module_end
SNMPv3
To configure an SNMPv3 module, set module_version to 3 and specify:
module_seclevel: Security level (noauth,authnoprivorauthpriv).module_secname: Security name.module_authproto: Authentication protocol (md5osha).module_authpass: Authentication key.module_privproto: Privacy protocol (aesodes).module_privpass: Privacy key, as needed.
Make sure that the OIDs begin with a dot. Otherwise SNMP modules will not work.
module_begin module_name snmp_noauth module_type generic_data_string module_snmp 127.0.0.1 module_version 3 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 module_seclevel noauth module_secname snmpuser module_end
module_begin module_name snmp_authnopriv module_type generic_data_string module_snmp 127.0.0.1 module_version 3 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 module_seclevel authnopriv module_secname snmpuser module_authproto md5 module_authpass 12345678 module_end
module_begin module_name snmp_authpriv module_type generic_data_string module_snmp 127.0.0.1 module_version 3 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 module_seclevel authpriv module_secname snmpuser module_authproto sha module_authpass 12345678 module_privproto aes module_privpass 12345678 module_end
The specific SNMPv3 configuration can be shared between Modules by taking it out of the Module declaration, in case it is the same for all (it can also be shared between Agents by moving it to the Satellite Server configuration file):
agent_name snmp address 127.0.0.1 seclevel authpriv secname snmpuser authproto md5 authpass 12345678 privproto des privpass 12345678 module_begin module_name snmp_authpriv_1 module_type generic_data_string module_snmp module_version 3 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 module_end module_begin module_name snmp_authpriv_2 module_type generic_data_string module_snmp module_version 3 module_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 module_end
For component group creation (including SNMPv3) see “SNMP wizard”.
Default Satellite Server configuration file for SNMPv3:
You will need to set your own values and/or credentials, as well as change the necessary protocols or encryption methods. You will need to restart PFMS server for the new configuration values to be read and added into the memory.
# Security level used for SNMPv3 messages (noauth, authnopriv or authpriv). #snmp3_seclevel authpriv # Security name used for SNMPv3 messages. #snmp3_secname # Authentication protocol (md5 or sha) for authenticated SNMPv3 requests. #snmp3_authproto sha # Authentication password for authenticated SNMPv3 request. #snmp3_authpass # Privacy protocol (des or aes) for encrypted SNMPv3 requests. #snmp3_privproto des # Privacy password for encrypted SNMPv3 messages. #snmp3_privpass
See also credential encryption with snmp3_credential_box token.
SSH Queries
SSH queries on Satellite servers installed on MS Windows® is still under implementation. PFMS development team is working on it.
Generic SSH command:
module_begin module_name GenericSSH module_type generic_data module_ssh 192.168.30.3 module_command ls /tmp | wc -l module_end
To enter a threshold, it must be done both in the text definition of the Module (module_min_warning, module_min_critical) and in threshold definition through the web interface:
module_begin module_name Latency module_type generic_data module_latency 192.168.70.225 module_min_warning 80 module_min_critical 120 module_end
Execution Modules can be created manually. The scripts or commands executed by the Satellite Server must be previously deployed and accessible by it. In this sense, it works in the same way as a module_exec of an Agent. Note that the use of module_exec may cause Satellite Server performance to become poor.
module_begin module_name Sample_Remote_Exec module_type generic_data module_exec /usr/share/test/test.sh 192.168.50.20 module_min_warning 90 module_min_critical 95 module_end
See also credential encryption with ssh_credential_box token.
Queries with plugins
From Pandora FMS version 7 onwards, plugins can also be added. Like these, you have to take into account that the plugins will be executed in the machine where the Satellite Server is running. Therefore, it will be necessary to implement in these plugins some method to connect to the remote machine that needs to be monitored. The advantage over the previous ones is their great flexibility. That way, you may implement conditions and other mechanisms for which a module_exec falls short. The syntax is the same as for Agents. An example of use of a plugin could be the following:
module_plugin /usr/share/pandora/remote_advanced_checks.sh 192.168.0.1
Credential boxes
Unless authentication is configured with private key and public key, SSH, WMI and SNMP 3 Modules require a username (< user > ) and password (< pass > ) to work. Both are registered in the main configuration file, satellite_server.conf, using credential boxes (credential_box ) with the following formats:
network/mask,user,password
network/mask,user,[[encrypted password|]]
SSH queries on Satellite servers installed on MS Windows® is still under implementation. PFMS development team is working on it.
For example:
credential_box 192.168.1.1/32,<user>,<pass1> credential_box 192.168.1.0/24,<user>,<pass2>
Searches in credential boxes are made from more to less restrictive masks.
Passwords can be encrypted using Blowfish in ECB mode. Make sure that credential_pass is set, otherwise the host name will be used as the default encryption password. The hexadecimal representation of the ciphertext must be surrounded by double square brackets:
credential_box 192.168.1.0/24,<user>,[[80b51b60786b3de2|]]
Console view of all Agents
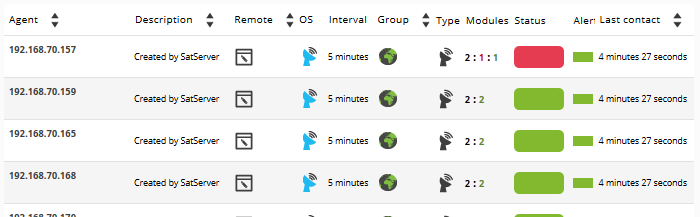
If Satellite Server configuration was successful, you should get an Agent view similar to this one:
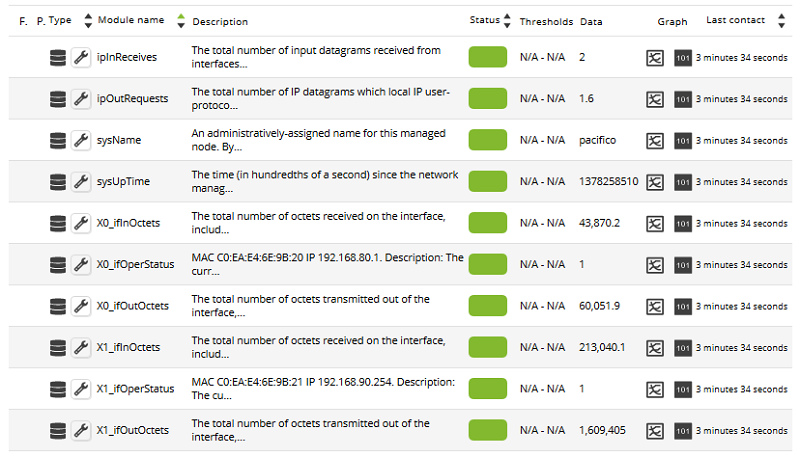
Generally, ICMP Modules (Ping and Latency) will be created in all machines, but in some of them SNMP and WMI type Modules may also be generated. On machines with WMI enabled, the following Modules will be generated, if available. On SNMP enabled machines, the following modules will be generated, if available:
In the massive_operations section of Pandora FMS Console there is a special section devoted to the Satellite Server, where it is possible to perform several editing and deleting actions of Agents and Modules in a massive way.
SNMP exclusion list
When monitoring large networks, SNMP Modules that return invalid data can affect the performance of the Satellite Server, and drive other Modules to Unknown status. To avoid this, the Satellite Server can read an exclude list of SNMP Modules that will be discarded at startup before execution.
To create a blacklist, edit the configuration file /etc/pandora/satellite_server.conf and verify that snmp_blacklist is uncommented and configured with the path to the file where the Modules of the blacklist will be saved. Then run:
satellite_server -v /etc/pandora/satellite_server.conf
Restart the Satellite Server. The excluded list can be regenerated as many times as necessary.
The format of the excluded list is:
agent:OID agent:OID ...
For example:
192.168.0.1:.1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.27 192.168.0.2:.1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.27


 Home
Home