Monitoring with Software Agents
We are working on the translation of the Pandora FMS documentation. Sorry for any inconvenience.
Monitoring with Software Agents
The Software Agents are running on the operating systems from which they collect information, performing a check for each module.
The Software Agent's own directives are used to collect certain data directly from the operating system (eg CPU usage, memory, events, etc.), executing operating system's own commands following instructions from predefined scripts.
The Pandora FMS Dataserver processes and stores in the database all the information generated and sent in XML files by the software agents.
Configuration of Software Agents
All the configuration and parameters are stored in the pandora_agent.conf file, which is also installed locally together with your Software Agent. The basic configuration is dealt with in "Configuration of Pandora FMS Agents", the advanced configuration is explained below.
Local Settings
In the Software Agent configuration file the modules are defined with the following basic text structure:
module_begin module_name <your module name> module_type generic_data module_exec <your command> module_description <your description> module_end
For the Software Agent on MS Windows® and the module_name instruction, if you want or need to use extended ASCII characters (áéíóú, for example) you must use an external plugin or script. See plugin section for Software Agents.
Remote Configuration
To enable remote configuration, enable the parameter: remote_config 1 and restart the software agent.
In the Enterprise version it is possible to remotely manage the files of the Software Agents from the Pandora FMS Web Console. The configuration of each agent is stored in the Pandora FMS server in two files: <md5>.conf and <md5>.md5, where <md5> is the hash of the software Agent name. These files are stored respectively in:
/var/spool/pandora/data_in/conf
and
/var/spool/pandora/data_in/md5
Once remote agent configuration is enabled, any changes made locally to the configuration file will be overwritten by the configuration stored in the console. To return to local administration of the Software Agent, stop its service, reset remote_config to zero, and start the service again.
Custom fields
Custom fields allow you to add additional information to the agent. Custom fields can be created with the PFMS 1.0 API and the command set create_custom_field or through the Web Console in the menu Management → Resources → Custom fields → Create field.
- The options Enabled combo, Password type and Link type are mutually exclusive, that is, only one of them can be used (or none, default value).
- By activating the Display up front field, the information of the custom field will be displayed, if it has any value set, in the agent's overview. Additionally, it will be necessary to activate this token to send the Custom Fields information to the Command Center (Metaconsole).
- Enabled combo: This parameter allows you to activate the configuration of selectable parameters from a drop-down menu. Once activated, a new field will appear in the configuration window of the corresponding custom field to enter the combo values separated by commas.
- Password type: The value of the field (password) will be shown using asterisks in the Web Console.
- Link type: It allows you to add a custom field that will host a web link to be filled in by the Web Console or in a XML received by an agent. It is possible to include links in the custom fields of an XML in JSON format embedded with CDATA instructions
<![CDATA[…]]>. For example, if the JSON format of the link is:
["Web name","https://example.com"]
The XML would have this syntax:
<custom_fields> <name>![CDATA[web]]</name> <value>![CDATA[["Web name","https://example.com"|]]]</value> </custom_fields>
See “XML Validation”, the Security Architecture for the Tentacle protocol (mechanism responsible for delivering data in XML format to the PFMS Data server) and the Security Architecture for the PFMS Data server (limit the auto-creation of agents and set a password for the agent group each agent belongs to).
Custom fields can also be passed from the agent configuration file, using the tokens custom_fieldx_name and custom_fieldx_value, for example:
custom_field1_name Serial Number custom_field1_value 56446456KS7000
The custom field called Serial Number is created by default when installing PFMS and you may create as many custom fields as needed and of each different type (simple value, web link, password type and option list type). The order of the numerical identifier of each custom field is irrelevant, you just have to ensure that the name is exactly the same:
custom_field11_name Simple custom field name custom_field11_value Simple custom field value custom_field12_name Custom field Link type custom_field12_value ["Pandora FMS web site","https://pandorafms.com"] custom_field13_name Custom field Password type custom_field13_value My;Password; custom_field14_name Custom field Combo type custom_field14_value Two
In the custom fields Combo type, the value sent by the software agent must correspond exactly to one of its items, otherwise the value will not be changed.
Common Configuration Parameters
Most important parameters for the basic configuration of Software Agents:
- server_ip: IP address of the Pandora FMS server.
- server_path: Path of the incoming input folder of the Pandora FMS server, by default
/var/spool/pandora/data_in. - temporary: Folder, default
/tmp. - logfile: Software Agent log file, by default
/var/log/pandora/pandora_agent.log. - interval: Agent execution interval, by default
300seconds.
Password Protected Groups
By default, when an agent sends data for the first time to the Pandora FMS server, it is automatically added to the group that has been defined in the agent's configuration file.
is possibleIt is possible to set a password for a group, so an agent will not be added to a group unless the correct password is specified in the agent's configuration file.
To edit and add a group password go to Management menu → Profiles → Manage agent groups → click on group name.
To add a new agent to this group, edit its configuration file and add the following configuration option group_password and restart the agent software.
Modules in Agents and Software Agents
Module types
According to returned data:
- generic_data: Numeric.
- generic_data_inc: Incremental.
- generic_data_inc_abs: Absolute incremental.
- generic_proc: Boolean .
- generic_data_string: Alphanumeric.
- async_data: Async Numeric.
- async_string: Asynchronous Alphanumeric.
- async_proc: Async Boolean.
- Image module: use a text string type module (
generic_data_stringorasync_string) as a base. If the data contained in the module is an image encoded in base64, (data:imageheader) it will be identified as an image and will enable a link to a window to retrieve the image in the views. In addition, a content of the different images that make up the stored chains will be shown in their respective history.
Intervals in local modules
The local (or software agent) modules are all “based” on the interval of their agent. However, they can take values that are multiples of that base if you modify the module_interval parameter with an integer multiply greater than zero.
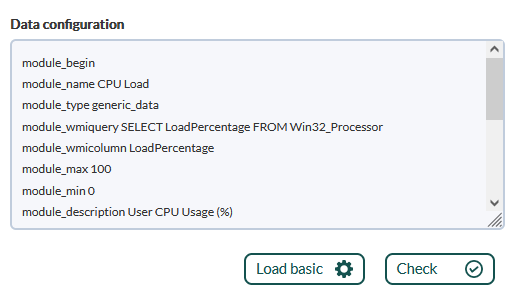
Module creation interface
![]() Functionality only for Enterprise version; the remote configuration of the respective Software Agent must be enabled.
Functionality only for Enterprise version; the remote configuration of the respective Software Agent must be enabled.
The creation of local modules in the console is done through a form where, in addition to the common configuration of all modules (thresholds, type, group, etc.), there is a text box where you can specify the configuration data to be established in the configuration file. Software Agent configuration.
- When clicking on the Load basic (template) button, the content of Data configuration will be deleted with a basic template that we must modify according to the need for monitoring.
- Once modified, clicking Check (syntax) will verify that the template syntax is still correct, however the rest of the commands will not be checked.
When a module is loaded from a local component, it can have macros. If you have macros, the configuration box will be hidden and a field will appear for each macro, see more information in Templates and components
Conditional monitoring
Postconditions
The Software Agent supports the execution of commands and scripts in postconditions mode. This means that you can perform actions depending on the value obtained in the execution of the module. The module_condition parameter is used for this, for example: module_condition < 20 add_processes.sh.
Preconditions
The parameter module_precondition allows you to evaluate a condition before the execution of the module and with the result decide whether the module should be executed or not, for example: module_precondition> 10 number_active_processes.sh .
Intensive monitoring
There are certain modules that have a special importance, such as processes or critical services in execution. In order to monitor cases more closely, there is intensive monitoring.
It consists of warning in a shorter interval that a serious problem appeared, without the need to reduce the general interval of the agent.
Configuration in Software Agent:
- interval: Mandatory, agent sampling time in seconds, it is the general interval for all local modules.
- intensive_interval: Time in which it will notify if there is any problem, and it will always be executed in this period and if it matches the condition, it will be notified in this period of time (otherwise the data will be sent in the interval).
Module configuration:
- module_intensive_condition = <value>: If the module returns the <value> indicated in this parameter, it will report in the interval intensive previously defined. Other operators that can be used are:
<,>,!=', a range of values(m,n)and=~.
Example
The sshd service is very important since it is used to connect by shell remotely, we need to monitor its working:
intensive_interval 10 interval 300
module_begin module_name SSH Daemon module_type generic_data module exec ps aux | grep sshd | grep -v grep | wc -l module_intensive_condition = 0 module_end
If the service fails, you will be notified in the next 10 seconds. If the service is up, you will be notified in the next 5 minutes, like normally (normal interval, 300 seconds).
Scheduled Monitoring
The Software Agent supports the definition of scheduled modules that are executed at the defined instants. The syntax used is the same as that of the crontab file.
Remote checks with the software agent
A Software Agent is capable of performing remote checks, substituting the main PFMS server and even distributing them to broker agents.
ICMP Checks
ICMP checks or pingare very useful to know if a machine is connected or not to a network.
Unix
module_exec ping -c 1 IP_dir> /dev/null 2>&1; if [$? -eq 0 ]; then echo 1; else echo 0; fi
MS Windows®.
module_ping IP_addr
Note: module_advanced_options enables advanced options for ping.exe.
TCP Checks
TCP checks are useful to verify whether a port of a host stay open and allow to find out whether an application connects or not to the network.
UNIX
With the nmap command and its configuration parameters in the command line, to an IP address check whether port 80 is open (response waiting time of 5 seconds):
module_begin module_name PortOpen module_type generic_proc module_exec nmap 192.168.100.54 -p 80 | grep open > /dev/null 2>&1; echo $?; if [ $? == 0 ]; then echo 1; else echo 0; fi module_timeout 5 module_end
MS Windows®
Parameters must be specified in:
- module_tcpcheck: Host to be checked
- module_port: Port to be checked
- module_timeout: Timeout for the check
Example:
module_begin module_name TcpCheck module_type generic_proc module_tcpcheck 192.168.100.54 module_port 80 module_timeout 5 module_end
SNMP Checks
SNMP checks are common in monitoring network devices to check the status of interfaces, input/output bytes, etc.
Unix example
module_exec snmpget IP_dir -v 1 -c public .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.148 | awk '{print $4}'
Example on MS Windows®
module_snmpget module_snmpversion 1 module_snmp_community public module_snmp_agent 192.168.100.54 module_snmp_oid .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.148 module_end
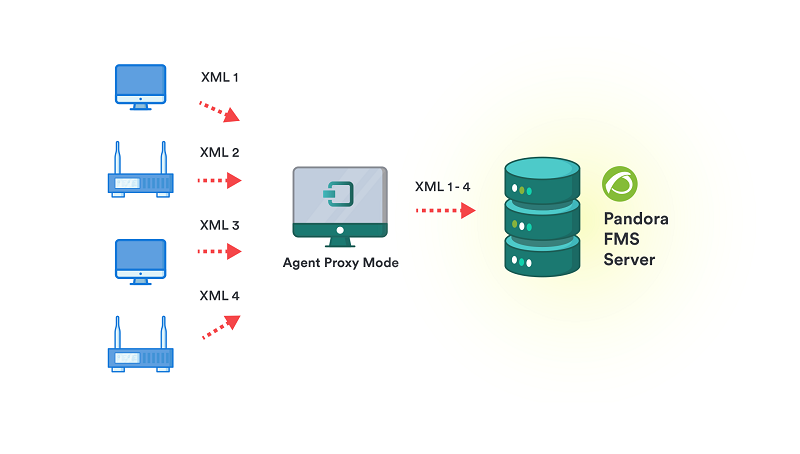
Proxy Mode
To use the proxy mode of the Pandora FMS agent in Linux/Unix® it cannot be executed by the root user, therefore a special installation of the Pandora FMS agent is necessary. To do so, see Custom Agent installation.
This mode allows redirecting the data files generated by other Software Agents to the Pandora FMS server. The software agent that acts in Proxy Mode can also perform monitoring tasks.
- server_ip: Pandora FMS server IP address.
- proxy_mode: On (1) or Off (0).
- proxy_max_connection: number of concurrent proxy connections, by default 10.
- proxy_timeout: response timeout for the proxy, default 1 second.
- proxy_address: address on which the proxy listens.
- proxy_port: port on which the proxy listens.
Broker Mode
The Software Agents Broker Mode allows a single agent to perform checks and manage the configuration as if it were several different agents.
 When Broker Mode is activated in a Software Agent, a new configuration file is created. From then on, the original Software Agent and the new broker will be managed separately with their independent configuration files, as if they were two completely separate Software Agents on the same machine.
When Broker Mode is activated in a Software Agent, a new configuration file is created. From then on, the original Software Agent and the new broker will be managed separately with their independent configuration files, as if they were two completely separate Software Agents on the same machine.
To create a Broker, add one or more lines with the parameter broker_agent <broker_name> (one line for each Broker).
In the Pandora FMS Web Console the Brokers are seen and managed as independent agents.
- The modules that save data in memory between executions (
module_logeventandmodule_regexpon MS Windows®) do not work when broker agents are configured. - Broker mode instances cannot use collections.
Inventory with software agent
For more information visit the section Local inventory with software agents.
Log collection with software agent
For more information visit the topic Log collection and monitoring.
Remote actions by UDP
A Software Agent is capable of receiving remote requests and executing orders.
Keep in mind that UDP is by nature insecure (but efficient at sending messages without compromising a certain response).
To allow the PFMS server to send orders to the Software Agents under its charge, the following must be configured:
- udp_server: zero by default, set to one (1) to enable this functionality.
- udp_server_port: listening port in Software Agent.
- udp_server_auth_address: IP address of the Pandora FMS server
Restart the Software Agent for the changes to take effect.
ohAlthough it can be set to 0.0.0.0 to accept from all sources, such a practice is not recommended. If you have several PFMS Servers and/or use IPv6 you can put different IP addresses separated by commas. For example if you have in IPv6:2001:0db8:0000:130F:0000:0000:087C:140B and its abbreviation is 2001:0db8:0:130F::87C:140B use both separated by commas.
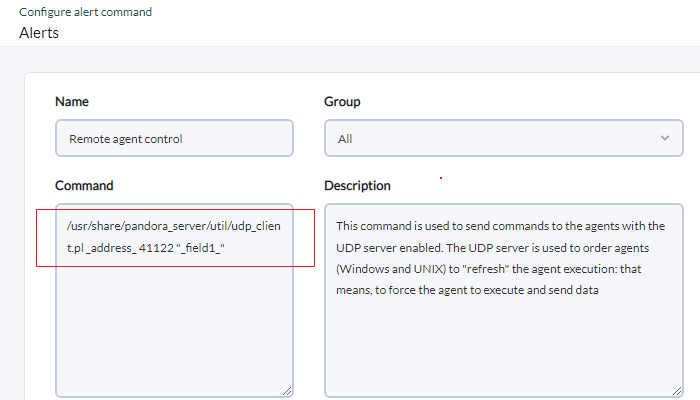
How to request Software Agents service restart
You must use the script located at:
/usr/share/pandora_server/util/udp_client.pl
It can be executed from the command line or used in an alert, through the command that comes preconfigurada in the Remote agent control console.
Custom Remote Actions
In addition to the Software Agent service restart action, custom actions can be specified.
process_<order_name>_start command
You can also create commands that call scripts to perform multiple remote actions with the click of a button.
Plugins in software agents
Unlike server plugins, executed by Pandora FMS server, Software Agent plugins report one or several modules at the same time.
Running on Windows systems
In MS Windows®, all plugins registered by default are programmed in VBScript, to execute them the cscript.exe interpreter is used.
Running on Unix systems
Unix plugins are located by default in the agent directory:
/etc/pandora/plugins
Management of Software Agent plugins from the Console
Management of advanced Software Agent plugins from the Console
Version NG 750 or later.
It is possible to add a token in the agent plugins configuration that when enabled allows the option to 'encapsulate' the plugin definitions inside the module_begin and module_end tags.
This enabled token allows you to insert configuration blocks such as module_interval or module_crontab, among others.
How to create custom plugins for Software Agent
Plugins can be created in any programming language. Only the general rules and specific rules should be taken into account for its development.
Be sure to end the output of the new plugin (if it is a script) with an errorlevel 0 or the agent will interpret the plugin as having an error and unable to run the job.
Using Nagios plugins from Software Agent
Nagios has a large number of plugins that you can use with Pandora FMS. One way to do this is to use the remote plugins with the Plugin Server, using the Nagios compatibility.
Monitoring with KeepAlive
The KeepAlive module can only be created from the Console, even if remote configuration is not enabled and it does not leave any trace in the pandora_agent.conf file.
A unique module in Pandora FMS is the type called keep_alive, used to alert if a Software Agent has stopped sending information.
You must go to the modules tab (Management → Manage agents → click on agent name → Modules).
Click Create module and select Create a new data server module → Create → enter the name of the new module → Create.
Monitoring command snapshots (Command snapshots)
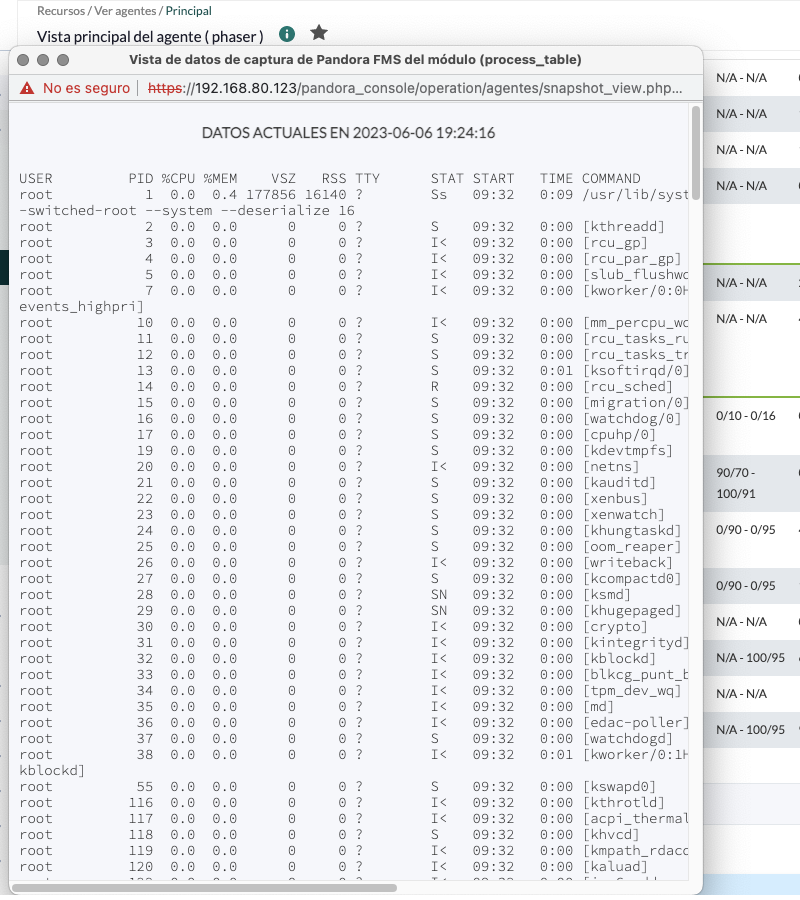 Commands with long output, such as
Commands with long output, such as top or netstat -n can be fully captured by a module and reproduced as-is. The module must be configured as text type, example:
module_begin module_name process_table module_type generic_data_string module_exec ps aux module_description Command snapshot of running processes module_group System module_end
- For this to work like this, you have to properly configure both the Pandora console (setup) andthe agent that collects that information, making sure that it is raw text.
- In the Console, the Command line snapshot option must be enabled.
Monitoring and visualization of images
This method allows defining modules of the string type (generic_data_string or async_string) that contain images in text format with a base64 encoding, being able to display said image instead of a specific result.
For example:
#!/bin/bash echo "<module>" echo "<name>Actual leader</name>" echo "<type>async_string</type>" echo "<data><![CDATA[data:image/jpeg;base64,/9j/4AAQSkZ....]]></data>" echo "</module>"
Write that content to a file on the agent (or distribute by collections) and run it like this:
module_plugin <complete path to the file>
Windows Specific Monitoring
- If the process name contains white spaces do not use
“ ”. - The process name must be the same as the one displayed in the Windows Task Manager (
taskmngr), including the extension.exe. - It is important to respect upper and lower case letters.
Process monitoring and process watchdog
Process monitoring
The module_proc parameter checks if a certain process name is running on this machine. Example:
module_begin module_name CMDProcess module_type generic_proc module_proc cmd.exe module_description Process Command line module_end
The parameter module_async yes must be added:
module_begin module_name CMDProcess module_type generic_proc module_proc cmd.exe module_async yes module_description Process Command line module_end
Process watchdog
The Watchdog functionality for MS Windows® allows to restart an interrupted process, example:
module_begin module_name Notepad module_type generic_data module_proc notepad.exe module_description Notepad module_async yes module_watchdog yes module_user_session yes module_start_command "%SystemRoot%\notepad.exe" module_startdelay 3000 module_retrydelay 2000 module_retries 5 module_end
Service monitoring and service watchdog
Service monitoring
The module_service parameter checks if a certain service is running on the machine. The definition of a module using this parameter would be:
module_begin module_nameService_Dhcp module_type generic_proc module_service Dhcp module_description Service DHCP Client module_end
To notify immediately when a process stops working, the parameter module_async yes must be added (see common rules at the beginning of the Windows section):
module_begin module_nameService_Dhcp module_type generic_proc module_service Dhcp module_description Service DHCP Client module_async yes module_end
Services Watchdog
It works in a similar way to the Process Watchdog. Example:
module_begin module_name ServiceSched module_type generic_proc module_service Schedule module_description Service Task scheduler module_async yes module_watchdog yes module_end
The watchdog definition for services does not require any additional parameters like the process parameter, because that information is already inside the service definition.
Monitoring of basic resources
When installing the PFMS Software Agent for MS Windows® the necessary basic modules are included, some of them come active and others must be activated by Remote Configuration (or locally editing the agent's .conf file).


 Home
Home